What Is a Glossary?
A glossary is a set of words or phrases that are considered to be technical or subject-specific terms or brand keywords (e.g. slogans or SEO keywords). Each word is listed in its source language along with its translation in the target languages.
A glossary isn’t a necessity from the translator’s point of view, but it does indicate the client’s preferred translation for a given word when the context allows it. The translator is the sole judge of whether or not the suggestion is relevant.
An example of a glossary
| fr-fr | en-us | es-es |
| jupe | skirt | falda |
| pantalon | pants | pantalones |
| T-shirt | T-shirt | T-shirt |
| pull | sweater | suéter |
| chaussettes | socks | calcetines |
What Kind of Terms Make Up a Glossary?
The words
Above all, a glossary is made up of single words. These words will be recognised if they are spelled identically in the glossary and in the text to be translated.
Their simple variants will also be recognised: plurals, conjugations and agreements.
For example: glossary, glossaries
Groups of words and slogans
It can also be made up of groups of words or slogans. These groups of words will be recognised if they are spelled identically in the glossary and in the text to be translated. if there are variants, which is rarely the case, they will be recognised up to a maximum of 3 words.
For example: Borders end here.
If there are more than 3 words, the entries will not be recognised, unless they are absolutely identical in the glossary and in the text to be translated.
What Can't Be Included in a Glossary?
Phrases, enumerations and lists.
A glossary can never be made up of descriptive or complex phrases, or of enumerations / lists.
For example: Deliveries during the month of May may be delayed by the many public holidays in France.
The same word with different translations
It is inadvisable to include the same word several times with different translations. It can prevent the glossary from working correctly.
For example: shop = magasin / shop = commerce
How Do You Construct a Glossary?
A glossary must be created in an Excel or CSV file.
In order to create a glossary, you must start by listing all of the terms in the first column that you wish to include in the first language. In the second column, you should put all of the corresponding terms for the second language in the adjacent cell (Term A = Cell B1 / Term A’ = Cell C1).

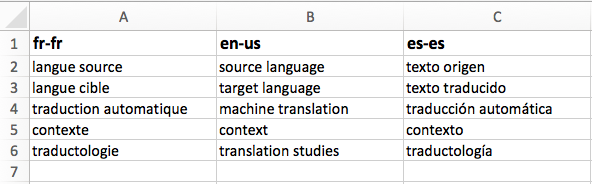
In the first cell of each column, it is necessary to add the appropriate language code for the language whose terms are included in that column. (You can find the codes here).
Important information
Maximum 5 words
In order to ensure correct performance, entries in a glossary should contain no more than 5 words. With entries that contain more than 5 words, it is more relevant to enter them in the translation memory.
Order of the columns
A glossary can be multilingual and the order of the columns is unimportant. A glossary where column 1 is in French and column 2 is in English can be use for projects from English to French and for those from French to English.
Incorrect entries
If the glossary contains incorrect entries (code language as the column header, a line break in an entry, an entry containing more than 5 words, etc.), the platform will reject your file when you try to import it.

